Vitamin C Cancer Treatment – Selective Targeting of Cancer Cells Without the Side Effects of Chemo
This clinic has long considered vitamin C to be a very important, even essential tool against cancer;
HOWEVER,
the other nutrients that accompany it have also been essential to the unsurpassed effects against cancer that our clinic has achieved over our 16 years of working with cancer patients. See our Cancer & Biochemistry videos for more information on each of those nutrients.
As the United States media becomes concentrated into ownership of the very few, we lose access to complete information about what is really happening in every field of human endeavor. Specifically, in the case of medicine, the problem of media blackouts on natural medicine is further compounded by the immense power of the pharmaceutical industry. That industry’s massive advertising budgets have had obvious influence over the editorial slant of many publications and other media. As a result, there are extraordinarily effective natural treatments for cancer that are never discussed by pharma-allied media, universities and politicians.
The chemist Linus Pauling was one of those extremely rare individuals to have actually won two Nobel prizes. Of Pauling’s prodigious life work, his research with high-dose vitamin C has probably had the most far-reaching effect in the lives of an increasing number of people.
Dr. Linus Pauling – Vitamin C Kills Cancer Cells
Dr. Pauling showed that for all the various kinds of cancer that one can acquire, Vitamin C treatments induce apoptosis. In other words, it kills cancer cells. It does this without inducing more pain or side effects, within weeks to months, and for a small fraction of the cost of chemotherapy. He showed that some go into remission completely on Vitamin C treatments (which we at Nature Works Best have verified, when used in combination with other nutrients in our own medical practice), and that for other more severe and late-stage cases, lengthening of life and easing of pain are the rule rather than the exception.
As a result of Pauling’s work and our own previous healing of cancer patients, we offer this therapy to cancer patients at any stage of their diagnosis. We provide high-dose intravenous Vitamin C treatments (with other anti-cancer nutrients) to these patients, and have seen them respond well. We have worked with Stage One through Stage Four cancers, from fairly benign to as life-threatening as pancreatic cancer. We have had cancer patients go into remission in as little as seven weeks (unusual) on our intravenous Vitamin C cancer therapy and other nutrient therapy alone. And we have had others with more intractable tumors, for whom the tumors never really went away, but rather became encapsulated in scar tissue or metabolically inactive, which rendered them neither growing nor shrinking, but more like tough shells of what they were, reduced from the high-dose blood supply that enabled their previous growth. The enormous majority of these patients are now stable and holding their own, including for many years after their active treatment at our clinic.

Vitamin C crystals. Image Source.
How Vitamin C Works Against Cancer
At some point in human development, we human beings lost the ability to make vitamin C in the body, and we must consume it in food. “Must” is a strong word, but it is known that vitamin C is essential for human life. Around the same time, humans seem to have developed Lipoprotein (a), abbreviated as Lp (a), likely because when famine reduces available vitamin C-rich food intake, Lp (a) then somewhat substitutes and compensates for it in stabilizing the extracellular matrix (ECM), which is the support structure surrounding our cells. This seems to make tissue resilient against cancer. But there is a downside. When we are deficient in vitamin C, Lp (a) seems to create atherosclerotic plaques. Vitamin C helps with both of these issues: strengthening the ECM and as an obstacle to atherosclerotic plaque formation. But very importantly for our work, vitamin C is very helpful against cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4948959/
That research found this:
In summary, the present study shows that vitamin C is an effective inhibitor of cancer metastasis in mammals lacking vitamin C synthesis and expressing Lp(a). In this context it is of interest that the mouse model used in this study mimics human metabolism with respect to these two important characteristics. While ECM impairment is a precondition for cancer growth and expansion, the prevention of ECM degradation and its reconstitution have not been a focus of therapeutic cancer research. In the absence of pharmacological stimuli for ECM growth and repair, vitamin C should be considered as the most effective option in cancer prevention and therapy. Clinical and epidemiological data support this approach. Vitamin C deficiency is common in advanced cancer patients and low plasma levels of this vitamin are associated with shorter survival of cancer patients.
One reason that vitamin C has such strong effect in making our ECM resilient against cancer is that vitamin C is necessary – not a luxury, but a necessity – for formation of collagen. Along with lysine and proline, two important co-factors for production of human collagen, producing resilient tissue is one of the two main strategies in use of vitamin C in cancer. It seems to prevent new metastases from gaining a foothold.
The other main strategy is this: Another main function of vitamin C against cancer is that when it is given intravenously, it produces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the extracellular tissue. This evenly distributed H2O2 has been shown to selectively attack cancer cells, which are more vulnerable to oxidative stress from the hydrogen peroxide that selectively targets cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1224653/
You may wonder two things at this point:
Q) Isn’t vitamin C an anti-oxidant? The above implies that it is pro-oxidant.
Ah, yes, but vitamin C is anti-oxidant in low dose. In high dose, it has been shown to be pro-oxidant, which has killed cancer cells. And…
Q) How can vitamin C selectively target cancer?
Normal cells have an enzyme, catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water, both of which are healthy and harmless to normal cells. However, cancer cells are characterized in part by lacking this enzyme catalase. Therefore, cancer cells are vulnerable to the oxidative damage coming from hydrogen peroxide in the immediate vicinity of the cells. This is how a cancer cell can be killed, while a normal cell near it can thrive. This is why you don’t see cancer patients who have chosen a path of vitamin C treatment losing their hair, or vomiting, or feeling more ill. In fact, they generally feel better with vitamin C treatment.
Now let’s look at a number of cancers, alphabetically, and see how vitamin C helps fight each of those cancers.
Bladder Cancer
For example, bladder cancer is characterized in part by a loss of a nucleotide base, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, which is an important component of our DNA. When this naturally occurring biochemical is reduced or destroyed, then we are at higher risk for bladder cancer. Researchers found that vitamin C helps to restore this important biochemical. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6045833/
When vitamin C was combined with proline, lysine and arginine, as well as greet tea extract, it was helpful to inhibit critical steps in proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6045833/
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer cells were destroyed when vitamin C was combined with selenium, when the combination released lactate dehydrogenase, leading to apoptosis. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33723142/
Researchers found that vitamin C produced collagen, which tended to wall-off or encapsulate a tumor from the rest of the body. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9531273/
Also, vitamin C tends to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition, which has been useful against breast cancers. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6753468/
There are multiple mechanisms by which vitamin C exerts its anti-cancer effects, both immune-mediated, via T-cell enhancement, and pro-oxidative. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.aay8707
Also, vitamin C worked synergistically with the chemotherapy drug oxaliplatin against breast cancer cells. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35214139/
Cervical and Uterine Cancers
This study showed that cancer-promoting effects of, estradiol, a kind of estrogen, were found to be opposed by the effects of vitamin C. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2378080/
Vitamin C intake was correlated with lower incidence of many kinds of cancer, including uterine cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8812486/
When vitamin C is used in combination with other co-factors known to build collagen, cervical cancer results were significantly improved. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25574189/
Colorectal Cancer
Vitamin C directly killed certain kinds of colorectal cancer cells. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4778961/
Vitamin C was helpful to break down resistance to treatment in some kinds of colorectal cancers. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10045351/
Vitamin C was observed to suppress proliferation and to induce apoptosis in certain kinds of colorectal cancers. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7714606/
Gastric and Esophageal Cancers
High-dose vitamin C decreased the number of esophageal cancer tumors in rats. https://www.scielo.br/j/acb/a/5XrddL6DFGLS4tg4434LXTc/?lang=en
H pylori bacteria can be pro-cancerous. Vitamin C helps to protect the gastric mucosa that lines the stomach from colonization from H pylori and from pre-cancerous changes to that mucosa. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7503565/
Leukemias and Lymphomas
Vitamin C killed cancer cells in leukemia and lymphoma cell lines. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8330290/
Vitamin C killed precursor cells to acute myeloid leukemia and other leukemias, without harming normal human cells. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26264692/
Liver and Biliary Tract Cancers
Vitamin C was shown to cause regression of pulmonary metastases from liver cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4541681/
Vitamin C preferentially kills cancer stem cells in liver cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5871898/
Vitamin C killed bile duct cancer cells via reactive oxygen species. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28385602/
Lung Cancer
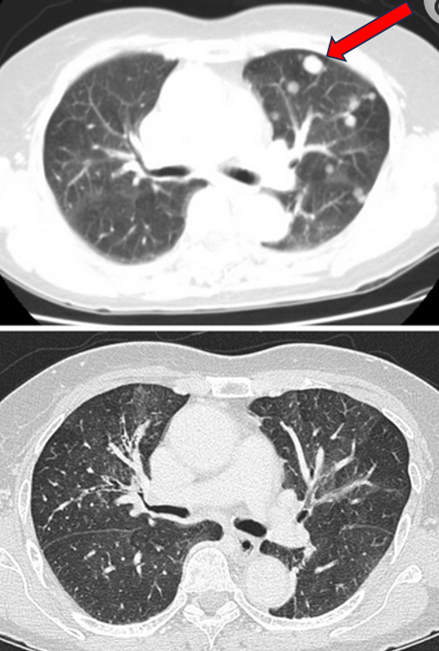
Multiple lung nodules disappeared after high-dose IV vitamin C treatments.
Top: before photo; Bottom: after photo.
Oil from the peel of mandarin orange showed significant anti-tumor activity without toxicity. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29560978/
Lung cancer was one of several types of cancer shown to be inversely correlated with vitamin C intake. Positive dose response was shown 63 health conditions over 76 meta-analyses. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35291895/
Ovarian Cancer
Vitamin C was found to be effective against ovarian cancer with an outstanding safety profile. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24500406/
Vitamin C’s effect against ovarian cancer was enhanced by heat therapy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36288898/
Pancreatic Cancer
High-dose intravenous vitamin C kills pancreatic cancer cells, while sparing normal cells. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36288898/
The mechanisms of vitamin C against pancreatic cancer includes the formation of hydrogen peroxide extracellularly. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4895694/
Vitamin C was combined effectively with a common chemotherapy drug for use in pancreatic cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3587047/
Prostate Cancer
Intravenous vitamin C killed prostate cancer cells by autophagy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22205155/
Vitamin C intake was correlated with lower incidence of many kinds of cancer, including prostate cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8812486/
Skin Cancer
Vitamin C inhibits the growth of melanoma by arresting the cell cycle and killing melanoma cells. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17119452/
Vitamin C promotes cell cycle arrest in oral squamous cell carcinoma. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7298137/
Thyroid Cancer
Vitamin C kills thyroid cancer cells, by way of reactive oxygen species. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31285773/
Vitamin C released iron from ferritin, which led to generation of reactive oxygen species, which had effect against thyroid cancer. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33714759/
Cancer in General
Vitamin C intake was correlated with lower incidence of many kinds of cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8812486/
Several types of cancer were shown to be inversely correlated with vitamin C intake. Positive dose response was shown 63 health conditions over 76 meta-analyses. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35291895/
In the 1970’s Ewan Cameron and Linus Pauling found that survival from cancer was prolonged with even oral doses of vitamin C. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC336151/
To incorporate conventional cancer treatments or not?
Patients are often nervous about the prospect of embarking on a treatment without the blessing of their oncologist or other physicians. To ease these concerns, we make clear to our patients that they are always free to pursue conventional treatments along with our treatments, if they choose to do so, whether simultaneously or consecutively. And of course, we coordinate care when asked to do so.
There are some benefits to be gained from the conventional cancer treatments, depending on the case, and we do encourage our patients to look into all of their options. In general, surgical removal of a resectable tumor has benefited our patients, when it is possible. However, many tumors are considered inoperable by surgeons. In that case, patients generally choose our treatments regardless, although thoe usually take longer without the added help of surgery.
All of the conventional therapies have been successfully combined with high dose intravenous Vitamin C therapy, without detriment to the patient. In fact, it has been found by many Vitamin C patients that it strengthens them when their other treatments leave them nauseated and weak. It also has had a markedly beneficial effect on the pain that accompanies cancer and the conventional therapies.
On the other hand, there are patients who have had enough of conventional medicine, or at least of conventional cancer treatments, and who choose to come to us exclusively. We do not turn these patients away either, and we have actually had our fastest successes usually with this type of patient.
Into Remission Without Quitting Smoking!
We have even had a throat cancer patient (cancer of the pharynx) go into remission without quitting smoking! Of course, we urged the patient to quit smoking, but fortunately the Vitamin C was more formidable than even the damage done by cigarettes.
If You Don’t Have Cancer, Here Are The Basic Ways To Prevent It
Do Regular Exercise!
Any kind of exercise, as long as it gets you moving, increases your heartrate, and is done at least a few times per week is of tremendous benefit.
Whole, Natural, Unprocessed Foods
Cancer prevention cannot be mentioned without discussing the massively beneficial effects of diet. One thing that even the mainstream now agrees on is that vegetables and fruits are essential to preventing cancer. The reason is simple: these are the foods that our ancestors thrived on, and on which they were able to avoid the debilitating chronic diseases that plague our contemporary populations. These are also, not so coincidentally, the foods from which our ancestors derived most of their Vitamin C.
Don’t Eat Sugar
Avoiding sugars and other processed foods is also very important, because such foods generally weaken immune system defenses against cancer, and overload the body with free radicals, substances that set into motion the chain of cellular-level events that lead to cancer, if unchecked.
However, here is a little-mentioned but very important thing to consider with regard to cancer prevention:
Get Enough Sleep
A brain chemical called melatonin is essential for at least two reasons: it enables the brain to go into the sleep state and stay there all night. It is also one of the most powerful fighters of free radicals in our bodies. That means that while we sleep melatonin is fighting off pre-cancerous changes before they can take hold. Cancer has long been observed to be more prevalent among nightworkers, especially those who must have strong lights shining during the night, than others. This is most likely related to the fact that melatonin shuts off when strong light hits the eyes.
—
Please see our Cancer & Biochemistry videos for further information on the role of nutrients with regard to cancer.
Have any questions about Vitamin C or anything else regarding our treatments? Comments? Let us know your thoughts below!


8 Comments